Operational Automations
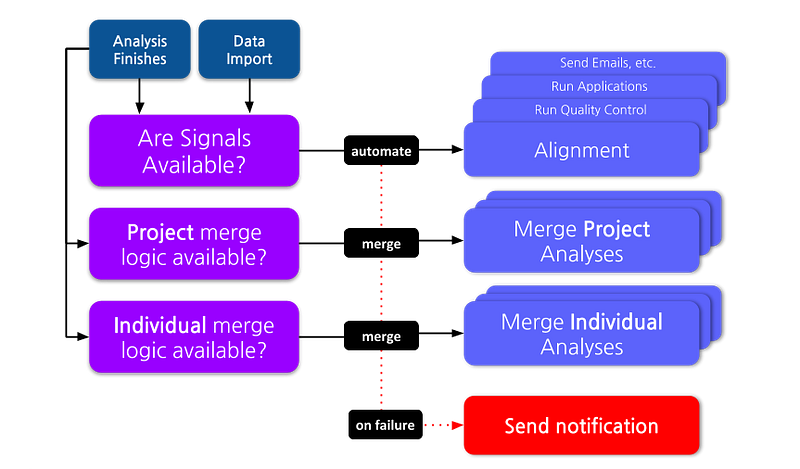
🤖 Once you have set up your Isabl instance and created a few applications you can now automate your processes! In Isabl, this is achieved using signals.
Operational Signals
Registering Signals
Signals on Data Import
Signals on Analysis Status Change
Working with Signals
Running Signals Manually
Rerunning Failed Signals
Get Notified When Signals Fail

Last updated
Was this helpful?